Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Manabe, Kentaro; Sato, Kaoru
JAEA-Review 2020-068, 114 Pages, 2021/03
Radiation safety regulations have been currently established based on the 1990Recommendation by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) in Japan. Meanwhile, ICRP released the 2007 Recommendation that replaces the 1990 Recommendation. Thus, the Radiation Council, which is established under the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), has made discussions to incorporate the purpose of the 2007 Recommendation into Japanese regulations for radiation safety. As ICRP also has published effective dose coefficients for internal exposure assessment in accordance with the 2007recommendation, the technical standards are to be revised for the internal exposure assessment method in Japan. Currently, not all of the effective doses have been published to revise concentration limits for internal exposure protections of workers and public. The published effective dose coefficients are applied to radionuclides which are important in radiation protection for internal exposure of a worker. Thus, we review new effective dose coefficients as well as basic dosimetry models and data based upon Occupational Intakes of Radionuclides (OIR) parts 2, 3 and 4 that have been published from 2016 to 2019 by ICRP. In addition, issues are sorted out to provide information for revision of the technical standards for internal exposure assessment based on the 2007 Recommendations in future.
Endo, Akira
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 175(3), p.378 - 387, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:72.2(Environmental Sciences)The International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) has been discussing to propose a new system of the operational quantities for external radiations based on protection quantities. The aim of this study is to provide a set of conversion coefficients for use in defining personal dose equivalent for individual monitoring. Fluence-to-effective dose conversion coefficients have been calculated for photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions and helium ions for various incident angles of radiations. The data sets comprise effective dose conversion coefficients for incident angles of radiations from 0  to 90
to 90  in steps of 15
in steps of 15 and at 180
and at 180 . Conversion coefficients for rotational, isotropic, superior hemisphere semi-isotropic and inferior hemisphere semi-isotropic irradiations are also included. The conversion coefficients are used to define the operational quantity personal dose equivalent which is being considered by ICRU and utilized for the design and calibration of dosemeters.
. Conversion coefficients for rotational, isotropic, superior hemisphere semi-isotropic and inferior hemisphere semi-isotropic irradiations are also included. The conversion coefficients are used to define the operational quantity personal dose equivalent which is being considered by ICRU and utilized for the design and calibration of dosemeters.
Saito, Kimiaki; Kurihara, Osamu*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Takahara, Shogo; Sato, Tetsuro*
Radioisotopes, 65(2), p.93 - 112, 2016/02
Late information is introduced on dose evaluation due to external exposures which employ an important role in the exposures due to the Fukushima accident. First, merits and demerits of the currently used two methods, that is the estimation based air dose rates and the measurements using personal dosimeters, are discussed indicating some basic data after a fundamental concept of external dose evaluation is provided. Next, main activities are summarized on external dose measurements and evaluations after the accident. Finally, a new trial on dose evaluation in introduced.
 rays and the exposure doses
rays and the exposure dosesSaito, Kimiaki; Endo, Akira
Radioisotopes, 63(12), p.585 - 602, 2014/12
The article provides the fundamental information necessary for the appropriate evaluation of exposure doses in the environment. The basic characteristics of environmental  rays from typical environmental sources are introduced; then, the dose conversion coeffcients for the public at different ages are summarized which were obtained from the simulation considering the basic characteristics of environmental
rays from typical environmental sources are introduced; then, the dose conversion coeffcients for the public at different ages are summarized which were obtained from the simulation considering the basic characteristics of environmental  rays. Further, the variations of environmental exposure doses due to a variety of factors, and the relation of exposure doses to measured air dose rates are discussed.
rays. Further, the variations of environmental exposure doses due to a variety of factors, and the relation of exposure doses to measured air dose rates are discussed.
Hato, Shinji*; Homma, Toshimitsu
JAERI-Data/Code 2005-006, 549 Pages, 2005/09
The OSCAAR computer code for use in probabilistic accident consequence assessment (Level3PSA) developed at JAERI has calculated dose to the public with internal dose conversion factors based on dosimetric models and biokinetic data provided in ICRP Publication 30. Since ICRP issued age-dependent biokinetic models for a limited set of radioisotopes as ICRP Publication 56, a new Human Respiratory Tract model, age-dependent biokinetic model for other radioisotopes and urinary and faecal excretion models were issued. ICRP has published age-dependent internal dose coefficients for a large set of radionuclides in its publications, but they provided only committed effective dose coefficients for inhalation and ingestion. Since OSCAAR estimated acute and late health effects for public, it needs internal dose coefficients for specific tissues and organs in arbitrary integration times.This report describes a code DSYS developed for calculating dose coefficients based on these new ICRP models. It also provides the internal dose coefficients for 54 radionuclides used in OSCAAR calculations.
Tran, V. H.; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Tsuda, Shuichi; Endo, Akira; Saito, Kimiaki; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
JAERI-Tech 2004-079, 37 Pages, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Mai, H. H.*; Duong, N. D.*; Kojima, Takuji
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 69(5), p.439 - 444, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:77.76(Chemistry, Physical)Characteristics of the polyvinyl chloride films containing 0.11wt% of malachite green oxalate or 6GX-setoglausine with 100 m in thickness were studied for use as routine dosimeters in radiation processing. These films show basically color bleaching under
m in thickness were studied for use as routine dosimeters in radiation processing. These films show basically color bleaching under  Co
Co  -ray irradiation in a dose range of 5 to 50 kGy. The sensitivity of the dosimeters and the linearity of dose response curves are improved by adding 2.5% of chloral hydrate [CCl
-ray irradiation in a dose range of 5 to 50 kGy. The sensitivity of the dosimeters and the linearity of dose response curves are improved by adding 2.5% of chloral hydrate [CCl CH(OH)
CH(OH) ] and 0.15% hydroquinone [HOC
] and 0.15% hydroquinone [HOC H
H OH]. These additions extent the minimum dose limit to 1 kGy covering dosimetric quality assurance in radiation processing of food and healthcare products. The dose responses of both films at irradiation temperatures of 20-35
OH]. These additions extent the minimum dose limit to 1 kGy covering dosimetric quality assurance in radiation processing of food and healthcare products. The dose responses of both films at irradiation temperatures of 20-35 C are constant relative to those at 25
C are constant relative to those at 25 C, and the irradiation temperature coefficients for 35-55
C, and the irradiation temperature coefficients for 35-55 C were estimated to be (0.43
C were estimated to be (0.43  0.01)%/
0.01)%/  C. The dosimeter characteristics are stable within 1% at 25
C. The dosimeter characteristics are stable within 1% at 25 C before and 60 days after irradiation.
C before and 60 days after irradiation.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Tsuda, Shuichi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Niita, Koji*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 106(2), p.137 - 144, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.71(Environmental Sciences)Radiological protection against high energy heavy ions has been an essential issue in the planning of long-term space missions. We calculated fluence to effective dose conversion coefficients for heavy ions using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System PHITS coupled with an anthropomorphic phantom of the MIRD5 type. The calculations were performed for incidences of protons and typical space heavy ions with energies up to 3 GeV/A in the isotropic and anterior-posterior irradiations. Based on the results, we propose a simple fitting formula that can predict the effective dose from almost all kinds of space heavy ions below 3 GeV/A within an accuracy of 30%.
Endo, Akira; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Iida, Takao*; Furuichi, Shinya*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 256(2), p.231 - 237, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.77(Chemistry, Analytical)Size distributions of  Cl,
Cl, 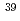 Cl,
Cl, 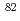 Br and
Br and 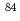 Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Sasamoto, Nobuo; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Hirayama, Hideo*; Shibata, Tokushi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.2), p.1264 - 1267, 2002/08
no abstracts in English
Kawai, Katsuo; Endo, Akira; Noguchi, Hiroshi
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-013, 66 Pages, 2002/05
Effective dose coefficients by inhalation and ingestion have been calculated for 334 nuclides, including (1) nuclides with half-lives 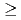 10min and their daughters that are not listed in ICRP Publications and (2) nuclides with half-lives
10min and their daughters that are not listed in ICRP Publications and (2) nuclides with half-lives  10min that are produced in a spallation target. Dose calculation was carried out using a nuclear decay database DECDC and a decay data library newly compiled from the ENSDF. The dose coefficients were calculated with the computer code DOCAP based on the respiratory tract model and biokinetic model of ICRP. The calculated results are presented as tables, which are the same forms as those in ICRP Publs.68 and 72. The complete listings of the dose coefficients are arranged on a CD-ROM, DoseCD, as indexed tables for inhalation of ten particle sizes, ingestion and injection into blood for workers and members of the public. The dose coefficients calculated in the present study are useful to calculate internal doses for a variety of radionuclides produced in high energy proton accelerator facilities.
10min that are produced in a spallation target. Dose calculation was carried out using a nuclear decay database DECDC and a decay data library newly compiled from the ENSDF. The dose coefficients were calculated with the computer code DOCAP based on the respiratory tract model and biokinetic model of ICRP. The calculated results are presented as tables, which are the same forms as those in ICRP Publs.68 and 72. The complete listings of the dose coefficients are arranged on a CD-ROM, DoseCD, as indexed tables for inhalation of ten particle sizes, ingestion and injection into blood for workers and members of the public. The dose coefficients calculated in the present study are useful to calculate internal doses for a variety of radionuclides produced in high energy proton accelerator facilities.
Sakamoto, Yukio; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
JAERI-Tech 2001-042, 29 Pages, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
JAERI-Data/Code 99-047, p.24 - 0, 1999/12
no abstracts in English
H.H.Mai*; Tachibana, Hiroyuki; Kojima, Takuji
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 53(1), p.85 - 91, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:44.25(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Manabe, Kentaro; Takahashi, Fumiaki
no journal, ,
The Atomic Energy Agency has developed a code for internal dose calculation as a fundamental technology for introduction of the 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection into the regulatory standards for internal exposure. The code provides two functions: calculation of committed effective doses for unit intake of radionuclides and estimation of intakes of radionuclides from individual monitoring data. The two functions are integrated by a graphical user interface. We will introduce an overview of the code, the status of implementation of biokinetic models published in April 2022, and a plan of integration of radiation absorption data based on the physique of reference Asian.